
- #CASH RECEIPTS JOURNAL MANUAL#
- #CASH RECEIPTS JOURNAL SOFTWARE#
- #CASH RECEIPTS JOURNAL CODE#
#CASH RECEIPTS JOURNAL MANUAL#
Refer to Section 85.15 of this manual for illustrations of budgetary entries to record and adjust estimated revenues. The entry would be reversed for In-Process debit amounts.
#CASH RECEIPTS JOURNAL CODE#
Entries posted to GL Code Series 71XX “In-Process” in treasury and treasury trust accounts also require an entry from the Office of State Treasurer (OST), as illustrated below, to clear the In-Process GL Codes.Ĭurrent Treasury Cash Activity (OST Only) (4310) The entries are for illustrative purposes only and should not be considered all inclusive. The entries in this section illustrate the recording of revenues and cash receipts in the accounting records. These entries are for illustrative purposes
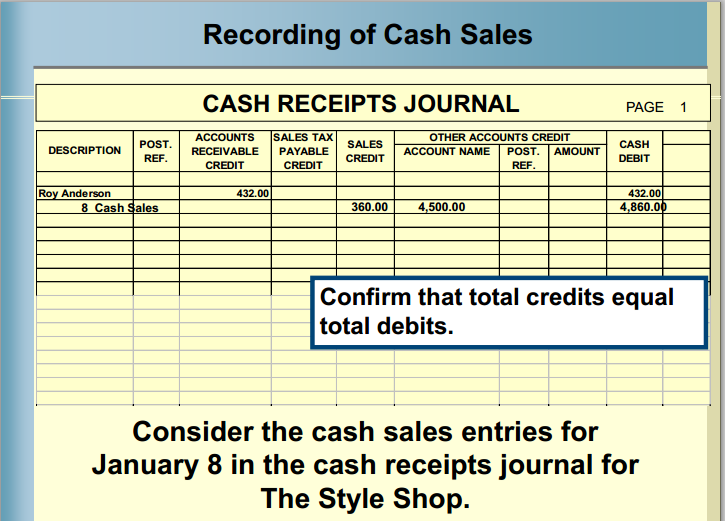
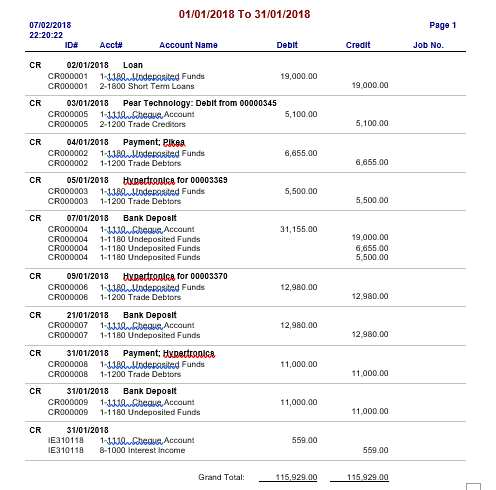
Revenue and Cash Receipts - Illustrative Entries The total of other accounts column is not posted to any account.Ĭonsider the following example for a better understanding of how entries in a cash disbursements journal are made and how the posting to accounts payable subsidiary ledger and general ledger is performed.85.24 - Revenue and Cash Receipts - Illustrative Entries
The totals of cash, inventory and accounts payable columns are posted at the end of the period (usually one month) to the relevant accounts in the general ledger. #CASH RECEIPTS JOURNAL SOFTWARE#
The individual amounts in the accounts payable column are posted daily (or immediately, if a computer software is used) to accounts payable subsidiary ledger and the individual amounts in other accounts column are posted daily (or immediately, if a computer software is used) to relevant accounts in the general ledger. The cash disbursements journal is posted to ledger accounts as follows: Posting entries from cash disbursements journal to ledger account Accounts payable column: The amount by which a supplier’s account is debited is written in this column. Examples include payment for inventory purchased on cash, payment for purchase of assets and payment of salaries, carriage and other expenses etc. Other accounts column: The cash paid for any purpose other than credit purchases is recorded in this column. As the discount taken form suppliers reduces our inventory cost, the inventory account in the general ledger is credited by the total of this column at the end of the period. Inventory column: Inventory column is used to enter the purchases discount allowed by suppliers of inventory. This amount must be net of any purchases discount received from suppliers of inventory etc. Cash column: The amount of cash paid is entered in cash column. Posting reference (abbreviated as PR) column is used to write the number of the account mentioned in account debited column. Posting reference (PR) column: All accounts in subsidiary and general ledger are properly numbered. Account debited column is used to enter the title of the account to be debited in the accounts payable subsidiary ledger or general ledger as a result of the payment of cash. Account debited column: Every cash transaction results in a credit to cash account and a debit to some other account. Payee column: The payee name (the person or entity to whom the payment is being made) is entered in this column. 
If the payment is made by a check, this column is used to enter the check number belonging to the payment.
Check number column: In large businesses, the payments are mostly made by checks. Date column: The date at which a payment is made to someone is entered in date column. The format of a cash disbursements journal and explanation of all the columns provided there in is given below:Įxplanation of the columns used in cash disbursements journal In cash disbursements journal, the cash payments are usually categorized as payments to accounts payable and payments for other purposes. Payment of cash for donations, charities and Zakat etc.įormat of cash disbursements/payments journal. Cash refunds for goods returned by customers. Payment of cash for the purchase of a tangible or intangible asset. Payment of cash for various expenses like rent, advertisement, carriage, wages and salaries etc. Payment of cash for previous credit purchases i.,e. The usual examples of cash outflows in a business are given below: All cash inflows are recorded in another journal known as cash receipts journal. In other words, a cash disbursements journal is used to record any transaction that includes a credit to cash. The cash disbursements journal (also known as cash payments journal) is a special journal that is used by a business to manage all cash outflows.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
